👋 Hey Friends,
It's Dr. Hetvi Soni here, and today we’re tackling a topic that concerns many of us—hair loss. But before that let me tell you HAIR FALL and HAIR LOSS are two different things, here’s how;
Hair Fall 🌿: This is part of the natural hair cycle. It’s completely normal to shed 50-100 hairs a day as part of the telogen (resting) phase. So, seeing a few strands in your brush or shower drain? That’s just regular shedding! 🚿✨
Hair Loss 🧬: This happens when the shedding becomes excessive or your hair stops growing back properly. If you notice thinning patches or bald spots, that’s when it shifts from natural hair fall to hair loss 😓. Hair loss is often caused by underlying factors like genetics, hormones, or medical conditions.
If you've ever found yourself worrying about the extra strands in your brush or noticing a thinning hairline, you're not alone! 😓 But don’t worry, because understanding why this happens is the first step to doing something about it. Let’s dive into the world of hair science, bust some common myths, and take a closer look at what’s really happening to those precious locks of yours 💁♀️💇♂️.
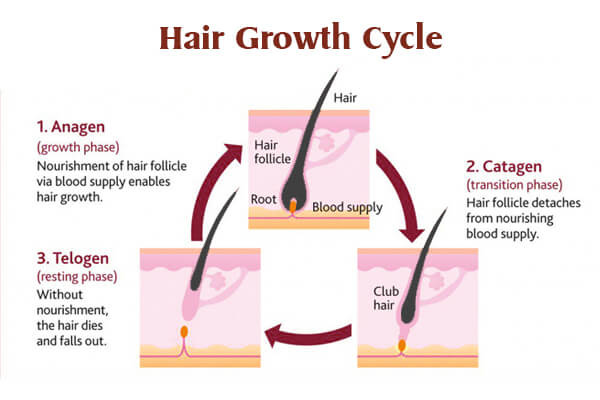
1. The Hair Growth Cycle: 🌱 What’s Normal Shedding?
Our hair goes through a natural cycle, and shedding is part of this process. But how does it all work? 🧐
Anagen (Growth Phase): This is when your hair is actively growing—this phase can last anywhere from 2 to 6 years 💪.
Catagen (Transition Phase): A brief, 2-week period where hair growth slows down.
Telogen (Resting Phase): This phase lasts about 3 months. During this time, your hair “rests” before shedding to make way for new growth.
Most of us shed about 50-100 hairs a day, and that’s totally normal! However, if you notice significantly more shedding over time, you may be dealing with one of the common causes below.
Sure! Here’s the first part of your newsletter: "🌿 Why Am I Losing Hair? 🧬 The Science of Hair Loss" with a well-structured explanation, emojis, and bullet points to keep it engaging.
2. Common Causes of Hair Loss: 🤔 What’s Behind It?
Several factors can lead to excessive hair loss. Let’s look at the most common ones:
👨👩👦 Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia): If hair loss runs in your family, you're more likely to experience pattern baldness, the most common type of hair loss in both men and women.
🌀 Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, menopause, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can trigger hair loss.
⚕️ Medical Conditions: Conditions such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata can also result in hair thinning or sudden bald patches.
🥗 Nutritional Deficiencies: Low levels of essential vitamins (like vitamin D, biotin, and iron) can weaken your hair.
💊 Medications: Certain drugs (e.g., those for cancer, high blood pressure, or depression) may list hair loss as a side effect.
😰 Stress and Trauma (Telogen Effluvium): Physical or emotional stress, surgery, or a sudden illness can push more hairs into the shedding phase.
Sure! Here’s the first part of your newsletter: "🌿 Why Am I Losing Hair? 🧬 The Science of Hair Loss" with a well-structured explanation, emojis, and bullet points to keep it engaging.
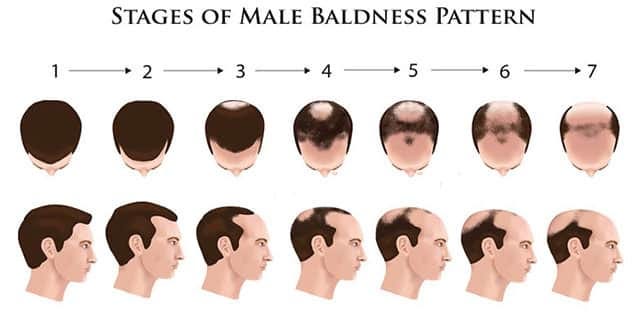
3. Pattern Baldness: 👨🦲👩🦳 The Genetics of Hair Loss
Pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss, affecting both men and women. Let’s break it down:
👨🦲 Male Pattern Baldness:
For men, hair loss often starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, eventually creating a U-shaped pattern around the sides and back of the head. This condition is largely genetic and can begin as early as the late teens or early 20s for some men. The main culprit? Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that shrinks hair follicles over time, slowing hair growth 😕.👩🦳 Female Pattern Baldness:
Women experience hair loss differently. Instead of a receding hairline, women often see diffuse thinning across the scalp, particularly at the part line. Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy 🤰, menopause 🌸, or conditions like PCOS, can speed up this process. While hair thinning in women is more gradual, it can still be distressing 😔. Luckily, treatment options exist to slow down the progression.
Both forms of pattern baldness are influenced by genetics and hormones 🧬, and while they can’t be cured, there are treatments available to help slow down or manage the hair loss process 💡.
4. Myths About Hair Loss: 🧐 What’s True and What’s Not?
Let’s clear up a few myths that might be causing confusion:
🚫 Myth: Wearing hats causes hair loss.
🟢 Truth: Wearing a hat won't make you bald. Hair loss happens below the scalp, not from external pressure.
🚫 Myth: Shampooing too much causes hair to fall out.
🟢 Truth: Regular washing is healthy for your scalp. However, harsh shampoos or over-styling might weaken your strands.
🚫 Myth: Cutting your hair makes it grow faster.
🟢 Truth: While a trim can reduce split ends, it doesn't affect the growth rate, which happens at the follicle level.
5. When to See a Doctor: 🩺 Knowing When It’s Serious
There are times when hair loss goes beyond normal shedding, and that’s when you should seek professional help. Some signs to watch out for:
Bald patches that suddenly appear 🕳️.
Excessive shedding lasting longer than 3 months.
Itching, redness, or pain on the scalp along with hair loss.
Don’t hesitate to talk to a doctor if you’re worried. Early intervention can often make a big difference in preventing further hair loss or even promoting regrowth 💡.
Final Thoughts: 🌟
Understanding the science of hair loss can take away some of the fear around it. Whether you’re dealing with male or female pattern baldness, stress-related hair loss, or something else, knowing the cause is the first step to finding the right solution.
In the next part of The Health Hub, we’ll explore effective treatments and lifestyle changes that can help you maintain strong, healthy hair and maybe even restore what’s been lost! 💪✨ Stay tuned for more expert tips and insights!
Until next time,
Dr. Hetvi Soni
Founder, The Health Hub 🌿